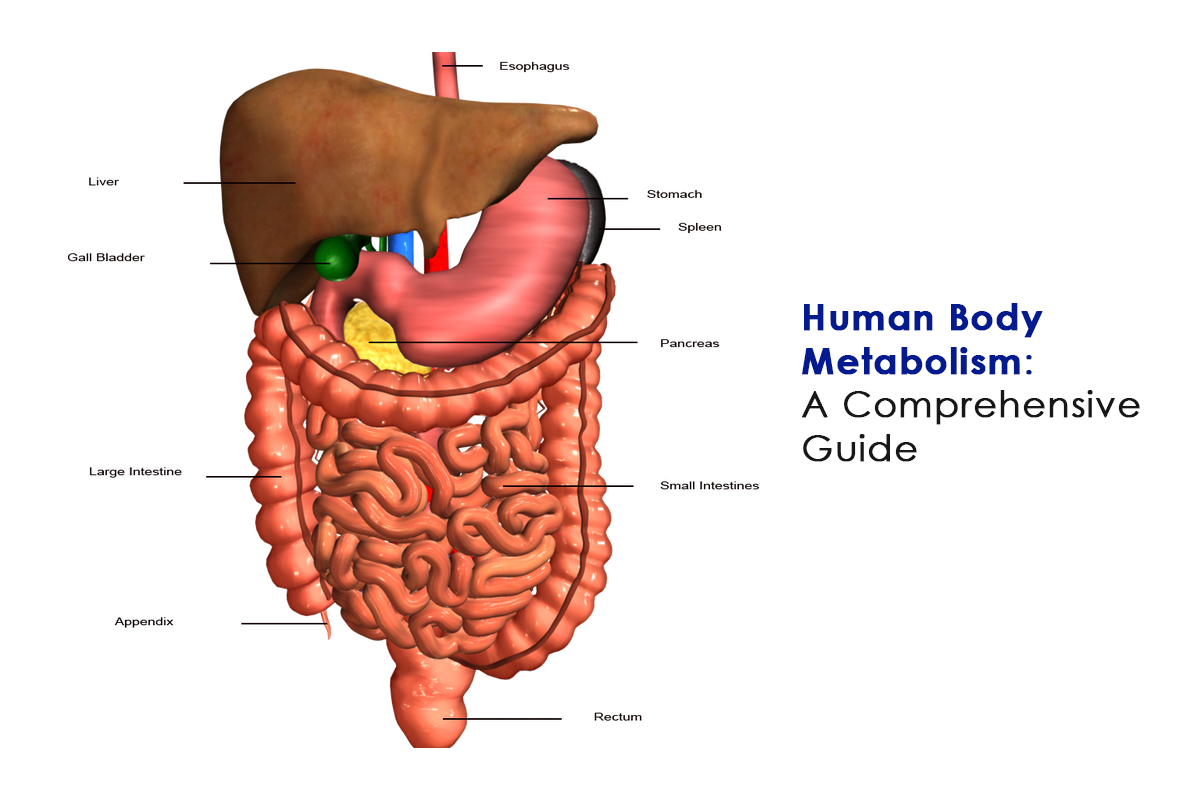
1. What is Metabolism?
Metabolism refers to all the biochemical processes that occur within the body to maintain life. It involves converting food into energy, building and repairing tissues, and eliminating waste. Metabolism consists of two main processes:
- Catabolism – Breaking down molecules (like carbohydrates, fats, and proteins) to release energy.
- Anabolism – Using energy to build and repair cells and tissues (e.g., muscle growth, bone repair).
- Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR): The number of calories your body needs at rest to maintain vital functions (breathing, circulation, cell production).
- Thermic Effect of Food (TEF): Energy used to digest, absorb, and metabolize food.
- Physical Activity: Energy expended through movement and exercise.
- Non-Exercise Activity Thermogenesis (NEAT): Energy burned through daily activities (walking, fidgeting, standing).
Key Components of Metabolism:
2. How Does Metabolism Work in the Human Body?
Metabolism is regulated by hormones, enzymes, and the nervous system. Key metabolic pathways include:
A. Carbohydrate Metabolism
- Digestion: Carbs break down into glucose.
- Insulin helps cells absorb glucose for energy.
- Excess glucose is stored as glycogen in the liver and muscles or converted to fat.
- Fats are broken into fatty acids and glycerol.
- Used for energy or stored in adipose tissue.
- Hormones like leptin and ghrelin regulate fat storage and hunger.
- Proteins break into amino acids.
- Used for muscle repair, enzyme production, and immune function.
- Excess amino acids are converted into glucose or fat.
- Thyroid hormones (T3, T4): Regulate BMR.
- Insulin & Glucagon: Control blood sugar.
- Cortisol: Affects fat storage and breakdown.
- Adrenaline & Noradrenaline: Increase energy expenditure.
B. Fat Metabolism
C. Protein Metabolism
D. Hormonal Control
3. Steps to Correct a Slow Metabolism
A sluggish metabolism can lead to weight gain, fatigue, and hormonal imbalances. Here's how to fix it:
A. Dietary Fixes
- Eat Enough Protein: Increases TEF and preserves muscle.
- Avoid Crash Diets: Very low-calorie diets slow metabolism.
- Stay Hydrated: Water is essential for metabolic reactions.
- Eat Regularly: Skipping meals slows metabolism.
- Include Healthy Fats: Omega-3s (fish, flaxseeds) support thyroid function.
- Strength Training: Muscle burns more calories than fat.
- High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT): Boosts metabolism post-workout.
- Get Enough Sleep: Poor sleep disrupts leptin & ghrelin.
- Manage Stress: High cortisol slows fat metabolism.
- Thyroid Test (TSH, T3, T4): Hypothyroidism slows metabolism.
- Check Insulin Resistance: High blood sugar affects fat storage.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Test cortisol, estrogen, testosterone.
B. Lifestyle Adjustments
C. Medical Check-Up
4. How to Boost Metabolism Naturally
A. Exercise Strategies
- Weightlifting: Builds muscle, which increases BMR.
- Cardio (Running, Cycling): Burns calories.
- NEAT (Non-Exercise Activity): Walk more, take stairs, stand often.
- Green Tea: Contains EGCG, increases fat oxidation
- Coffee: Caffeine stimulates metabolism
- Chili Peppers: Capsaicin raises body temperature
- Ginger Improves digestion & thermogenesis
- Apple Cider Vinegar May improve insulin sensitivity
- Cold Showers: Activates brown fat (burns calories for heat).
- Ice Water: Forces body to heat it up, burning calories.
B. Metabolism-Boosting Foods
C. Cold Exposure & Thermogenesis
5. Natural Remedies & Supplements
A. Herbs & Spices
- Turmeric (Curcumin): Anti-inflammatory, supports fat metabolism.
- Cinnamon: Helps regulate blood sugar.
- Ginseng: May improve energy and metabolic rate.
- L-Carnitine: Helps transport fatty acids for energy
- Omega-3: Reduces inflammation, supports thyroid
- Magnesium: Needed for ATP (energy) production
- B Vitamins: Help convert food into energy
- Chromium: Improves insulin sensitivity
- Green Tea Extract Boosts fat oxidation
- A healthy gut microbiome improves metabolism.
- Fermented foods (yogurt, kimchi, kefir) support digestion.
B. Supplements
C. Probiotics & Gut Health
6. Common Metabolism Killers (Avoid These!)
- Sugar & Refined Carbs: Spike insulin, promote fat storage.
- Trans Fats: Disrupt mitochondrial function.
- Chronic Stress: Raises cortisol, slows fat burning.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Reduces muscle mass and BMR.
- Alcohol: Slows fat metabolism, adds empty calories.
- ✅ Eat a balanced diet (protein, healthy fats, fiber).
- ✅ Exercise (strength training + cardio).
- ✅ Get enough sleep & manage stress.
- ✅ Consider natural supplements if needed.
- ✅ Avoid processed foods & excessive sugar.
Final Thoughts
Metabolism is a complex system influenced by diet, exercise, hormones, and lifestyle. To optimize it:
By following these steps, you can enhance your metabolic efficiency, improve energy levels, and maintain a healthy weight naturally.
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is for educational and informational purposes only and is not intended as medical advice. While the healthcare tips, product recommendations, and supplements mentioned are based on research and expert opinions, individual results may vary.Lactic Acid
HERE
LEAVE A REPLY
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Fast Delivery
Across West & East India
safe payment
100% Secure Payment
Online Discount
Add Multi-buy Discount
Help Center
Dedicated 24/7 Support
Curated items
From Handpicked Sellers




LEAVE A COMMENTs
Margaret Dickinson
"Great article! But how long does it take to 'fix' a slow metabolism? I've been eating healthy and exercising for 3 weeks but don't see big changes yet. Should I get my hormones checked?"
Edwin Robinson
"Interesting point about cold exposure activating brown fat. Does this mean ice baths are better than cold showers? Also, would intermittent fasting help or hurt metabolism in the long run?"🙌
Elena John
*"After having two kids, my metabolism was DEAD. Following these tips (especially strength training and more protein) helped me lose 20 lbs in 5 months—without starving myself. Life-changing!"*